7 min read
Technical & legislative challenges of cloud solutions for healthcare software
The eHealth industry’s growing at a breakneck pace, undoubtedly influenced by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and technological advancements, including the use of cloud solutions for healthcare. According to a report compiled by Market Data Forecast, this market is currently valued at $14.8 billion and is expected to grow to $29.5 billion by 2026. This implies a CARG (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 14.8% for the eHealth sector over the forecast period. What impact do cloud solutions have and will have on the growth of the eHealth sector? What technical and legal challenges connected to using the cloud are there in the healthcare market? Let’s try to answer these questions.
Cloud-based solutions – why are they so popular?
In recent years, we’ve seen digital transformation progressing in many sectors of the economy. The new reality is primarily associated with the increasingly widespread use of mobile applications, IoT, artificial intelligence, or cloud solutions. Importantly, migration to the cloud is increasingly becoming the basic technological strategy in many companies, regardless of their size. The healthcare industry, of course, also noticed its potential.
Sid Nag, research vice president at Gartner, said that “the ability to use on-demand, scalable cloud models to achieve cost efficiency and business continuity is providing the impetus for organizations to rapidly accelerate their digital business transformation plans. The increased use of public cloud services has reinforced cloud adoption to be the ‘new normal,’ now more than ever.”
Cloud solutions provide universal, convenient, and fast access to managed IT resources (e.g. having your own virtual private cloud, databases, orchestration tools, machine learning, monitoring services, and a lot more), requiring only minimal management with the provider. Thanks to them, we can create a modern working environment with primary advantages:
security,
efficiency,
scalability and elasticity,
cost-effective (pay-as-you-go),
possibility of advanced data analysis.
The implementation of cloud solutions in the medical industry is also a source of savings and allows healthcare facilities to focus primarily on key operational activities.
Types of cloud solutions in healthcare
The use of cloud solutions must be considered from two perspectives: distribution and access.
In case of distribution, we have:
- Infrastructure as a Service – in this model, the provider delivers IT infrastructure, and the client owns (and is responsible for) the operating system and deploys apps;
- Platform as a Service – in this second option, the provider delivers IT infrastructure and an operating system, while the client deploys applications;
- Software as a Service – the last option, in which the provider delivers IT infrastructure, operating system, and ready-to-use apps.
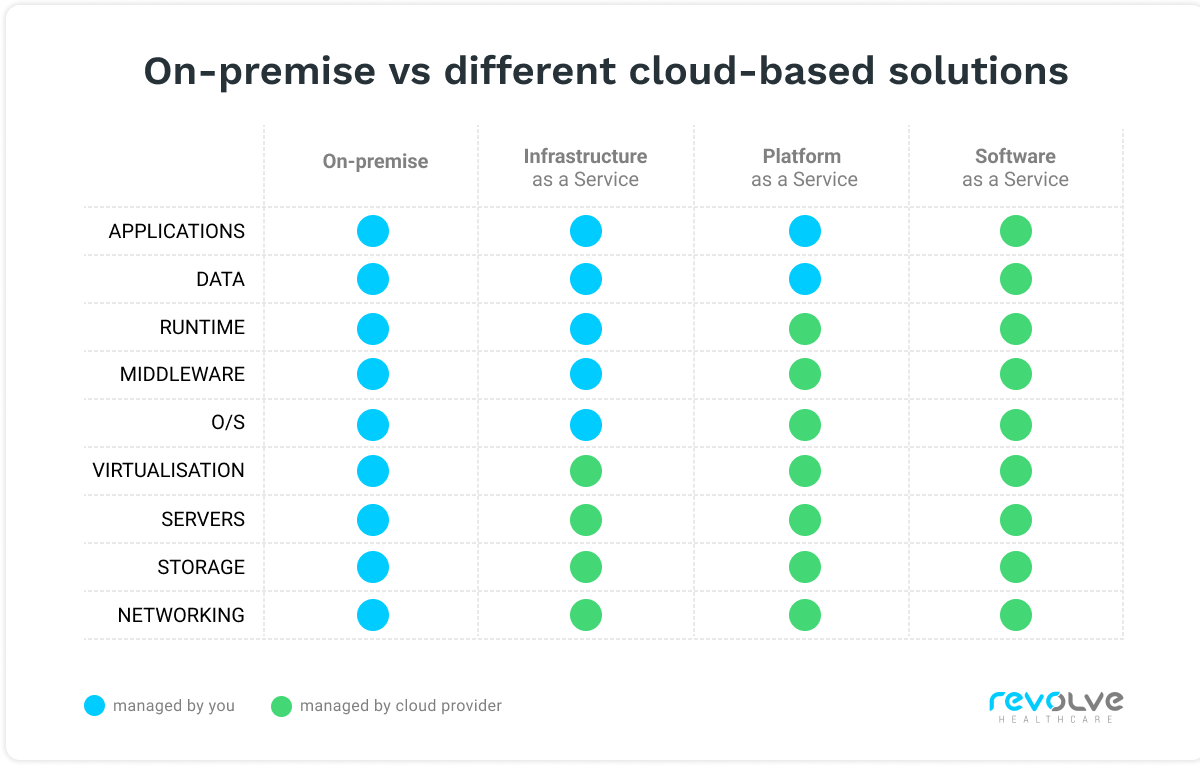
Comparison of on-premise to IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cloud options.
By cloud access, we can differentiate:
- Private cloud – only one client has access and the right to use it;
- Community cloud – a hybrid form of private cloud, multi-tenancy, which allows different entities to work on a common platform;
- Public cloud – in this case, computing services are offered by external providers over the public Internet, making them available to anyone who wants to use them or purchase them.
The choice of a particular cloud solution for healthcare software depends on many factors. However, the most important ones should include the best possible match between the service and software, data security, costs, effective operation, and scalability. In the medical industry, any downtime in data access means enormous losses, as does its failure due to a cyber-attack. Also, if you’re handling patient data, you need to be especially aware of how secure the chosen option is. Therefore, it matters whether a given cloud provider stores data and servers within or outside the EU.
What are the benefits of cloud computing in the healthcare industry?
- Seamless cooperation – cloud-based systems are available on demand, regardless of time and place. With cloud computing, data can be shared securely with all healthcare providers – doctors, nurses, and patients. They can remotely access test results, analyses and medical records. The cloud supports the diagnosis and treatment processes through the possibility of conducting remote consultations, rapid reporting on patients’ health status, necessary examinations, planned procedures or healthcare developments.
- Cost optimization ‒ cloud computing hosts a massive amount of information at a relatively low cost. The pay-as-you-go or subscription billing model ensures that you actually pay for what you use. You can expand the space if required, as clouds are fully scalable. In this way, the costs associated with maintaining and developing the IT infrastructure are reduced, and the funds obtained in this way can be used for further development of your medical applications or software.
- Smooth operation ‒ in healthcare, the speed of operation and access to information are crucial. Cloud computing provides efficient access to data by hosting servers in different countries and continents. Cloud-based tools can update and upgrade functions with minimal IT involvement.
- Scalability and elasticity ‒ healthcare providers operate in a dynamic environment. Cloud computing facilitates the use of technologies that support the doctors’ and medical staff’s daily work and are convenient for patients. We’re talking about electronic medical records, mHealth applications, patient portals or diagnostic IoT devices. The 24/7 availability makes healthcare providers need to powerfully scale their data storage and network requirements according to the ongoing demand for services. By choosing cloud computing, you can increase or decrease your storage needs depending on the current state of your healthcare software or application usage.
Cloud solutions for healthcare software – legislative challenges
The new digital reality in the medical sector means protecting patient data and ensuring its proper flow to improve diagnosis and treatment. Undeniably, the development of cloud technologies can help with this. First, however, you need to remember that the medical software and applications sector is subject to many legal regulations – different for the US and EU markets.
The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the MDR (Medical Device Regulation), and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) provide the legal framework for the processing of health data. Any company that produces digital health applications or software is referred to as a Data Processor or Data Controller in the EU or a Business Associate in the US.
As a contractor, this means that you are responsible for the technical correctness and security of your applications. If you are in the digital health industry, you must comply with several requirements for an application or software you are launching to be approved for use. You must protect your users’ data by implementing many security techniques, such as pseudonymization, anonymization, and encryption. While this is a time-consuming and expensive process, it’s essential.
It’s worth remembering that physical requirements, such as firewalls or load balancers, are usually provided by the cloud provider. They increase the level of security – as long as they are configured correctly. Technical requirements, on the other hand, are the responsibility of the software owner. To be compliant, you need to implement additional measures such as proper encryption and audit logs. These aren’t simple tasks and require the commitment of a skilled development team.
Therefore, making sure your own development processes comply with all the regulations or choosing an experienced and reliable software development company (if you consider outsourcing software development), is very important if you want to use cloud solutions for healthcare software. In some cases, it may also be necessary to involve lawyers to complete the documentation correctly.
If you want to learn more about data privacy and regulatory compliance for digital health software, we recommend checking out this blog.
Technical challenges of cloud solutions for healthcare
Notably, the increasing adoption of cloud solutions in healthcare has opened new “big data” opportunities to improve patient outcomes. In the past, paper patient records were the norm. This required storage space and generated problems in the form of an inability to turn data into valuable information – for example, predicting epidemics, detecting correlations in patients’ illnesses, analyzing the causes of diseases, or clarifying which treatment options are most effective for a given set of symptoms.
With the introduction of cloud computing, all medical data can be searched and analyzed using highly complex computer algorithms. This enables early detection and response to threats, improves the quality of medical services and the efficiency of medical facilities.
The main barrier to developing software and mobile medical applications in the cloud isn’t the limitations of the technology but the limited speed of its adaptation to the existing healthcare system. The traditional healthcare financing system mainly assumes direct contact between the patient and the doctor, making remote care challenging to implement. The solution to this problem is to regulate the legal issues related to remote care and, above all, to determine the source and method of its financing.
Apart from external conditions, the problem of adaptation of cloud technologies is related to the lack of adjustment to the needs of a specific healthcare unit, including physicians’ preferences and the existing infrastructure. To eliminate this limitation, it’s necessary to increase the participation of doctors and medical staff in migrating medical systems and applications to the cloud. In addition to adequately matching users’ expectations, this will also benefit from reliable verification of the available medical knowledge.
Cloud computing and the transfer of sensitive patient data also require an appropriate level of security. Both the data stored locally on devices and those transmitted over wireless networks should be encrypted. The cloud systems used should also correctly manage access to files.
Last but not least, medical applications and software, which impact the activities of doctors and medical personnel in terms of diagnosis or therapy, should have a properly designed, fault-tolerant user interface (UI). To this end, it’s essential to develop a detailed specification of all data use scenarios and an analysis of the risks associated with its misuse. This will help to secure data stored in the cloud appropriately, as well as to adapt to the legal requirements.
Summary
Software improvements in healthcare via the cloud are about more than just aggregating and sharing medical information from multiple computers anytime, anywhere, and on any mobile device. Also significant are the benefits of connecting medical centres and cloud users to share patient health data online. The use of cloud computing in healthcare looks bright in the near future. Older legacy systems need to be upgraded to deliver the expected levels of efficiency and scalability.
If you run a healthcare facility or develop medical software, you can achieve this transformation by moving to the cloud. However, you need to keep legal standards in mind and support yourself with an experienced team of developers, working according to ISO- compliant standards to ensure that the cloud you choose is the right one – and that you use it in the right way.
But here cloud providers also come with help to have your application compliant with e.g. HL7 FHIR specification that is about exchanging healthcare information electronically. Among other great cloud providers, Amazon AWS shared an example solution that can be used for free to fully meet the spec requirements (you can read more about this particular solution and HL7 FHIR in this article).

